Mitigating Complex DDoS Attacks on Digital Storefronts: Insights on the Latest DDoS Attack Trends
By Patrick Enderby, Sr. Product Marketing Manager
There are more digital touchpoints than ever before for most retail, hospitality, and food service organizations. Interactions with customers are increasingly happening online, away from traditional, physical Point of Sale (POS) systems which are still critical components for many of these organizations, enabling merchants to process sales transactions and manage inventory. However, the growth in e-commerce and online services means an increasing number of sales are being transacted online, creating an enticing target for cybercriminals.
One of the common forms of attacks e-commerce and web-facing services experience are Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks which continue to grow in complexity with multi-vector attacks leading in F5’s latest F5 Labs 2023 DDoS Attack Trends report. These attacks can cripple an organization's web storefront, disrupting digital transactions by overwhelming these properties with requests, exploiting vulnerabilities, abusing protocols/services, and resulting in crashes or substantial slowdowns preventing legitimate users and usage.
Additionally, DDoS attacks on e-commerce properties can have severe financial implications for businesses, with an average cost of $2.6 million in 2020, including direct costs of mitigating the attack and indirect costs associated with lost productivity, reputation damage, and customer loss, according to Accenture. Moreover, these attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with attackers leveraging amplification attacks and botnets to increase the volume of traffic directed at digital storefronts. It is essential that businesses take proactive measures to safeguard their digital infrastructure from DDoS attacks by implementing robust network security protocols and investing in cloud-based security systems.
F5 recently mitigated a modern, multi-layered, and highly distributed DoS attack aimed at overwhelming a company’s servers with massive amounts of traffic, making it difficult for users to access the site and interact with the organization. In this case attack traffic peaked at 120,000 requests per second (RPS).
Thanks to the advanced DDoS mitigation capabilities of F5’s new SaaS-based web app and API protection service, F5 Distributed Cloud Services, the attack was successfully mitigated, and the website remained operational throughout the attack. This attack was one of several DDoS campaigns that had been occurring over the prior few weeks and was attributed to a well-known hacking group.
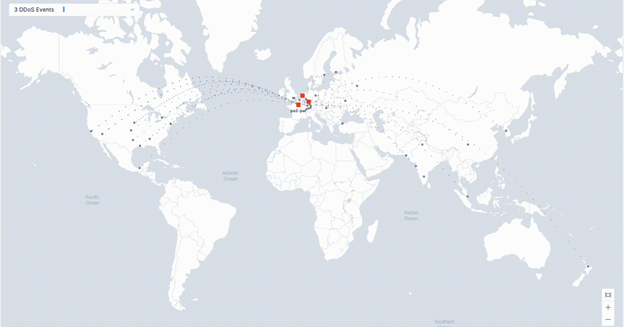
This specific DDoS attack originated from multiple global locations, as indicated by the grey dots on the map above, and was mitigated by F5 from its global points of presence represented by the red boxes. Application traffic was filtered, allowing only legitimate traffic through.
The attack was particularly challenging to detect and mitigate as it focused on the application layer (L7) and involved mimicking normal user behavior, utilizing multiple application attack vectors, and cycling through different source locations, IPs, and other attack components.
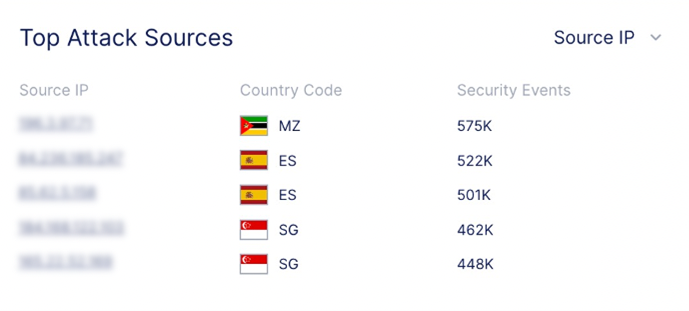
Top Source IPs from where the attack is originating from. The attack traffic is seen across several distributed IP addresses around the globe.

The specific TLS fingerprint associated with the majority of attack traffic in this attack scenario.
Only 3 TLS fingerprints were responsible for the attack. Unlike their lower-layer counterparts, application-layer DDoS attacks utilize the widely accepted TLS encryption, commonly used across the internet. F5 technology can identify and compare these fingerprints and reduce “fake traffic” - despite the traffic appearing to originate from 35 different IP addresses and 19 countries. Most of the attack traffic (72%) originated from a single TLS Fingerprint (shown above), which has been associated with Tofsee malware. Systems infected with this malware are used as part of a DDoS botnet.
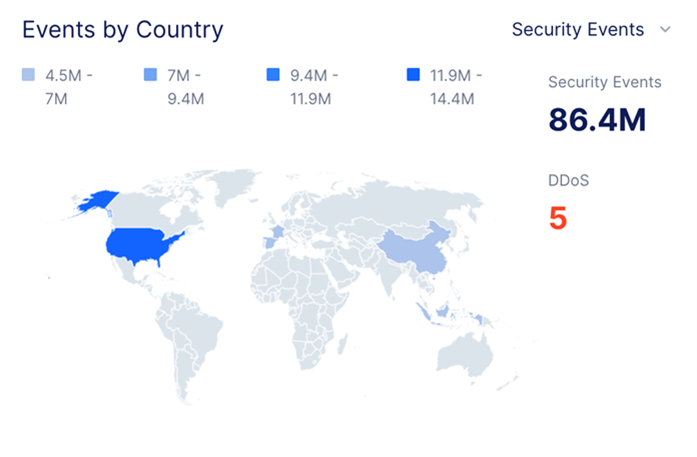
The attackers leveraged different geographies in hopes of finding a gap in geolocation protections.

Different HTTP methods and URL combinations were targeted during the attack.
F5 utilized several techniques to counter the attack, such as traffic filtering, IP intelligence, and rate limiting. This approach helped identify and block only malicious traffic while allowing legitimate traffic to reach the website. Moreover, real-time threat intelligence and L7 DDoS auto-mitigation capabilities were deployed to block parts of the attack in real-time without human intervention. This allowed F5 to remain ahead of the attackers and adjust its defense strategies quickly as the attack shifted across different locations, IP addresses, and attack paths.
Complex L7 DDoS attacks has become the new normal. To protect against these attacks, organizations must safeguard their infrastructure and applications against even the most sophisticated attacks by using a combination of traffic filtering, rate limiting, cloud-based DDoS scrubbing, real-time threat intelligence, and a solid disaster recovery plan.
This attack recap emphasizes the importance of having a multi-layered security infrastructure and a well-trained security team that can provide real-time support. For more insights on DDoS attack trends, refer to the F5 Labs 2023 DDoS Attack Trends report.
If your organization is experiencing a disruptive attack and needs emergency onboarding, leverage F5’s Distributed Cloud Services by contacting our emergency support line at (866) 329-4253 or +1 (206) 272-7969.